Windows 10
Introduction
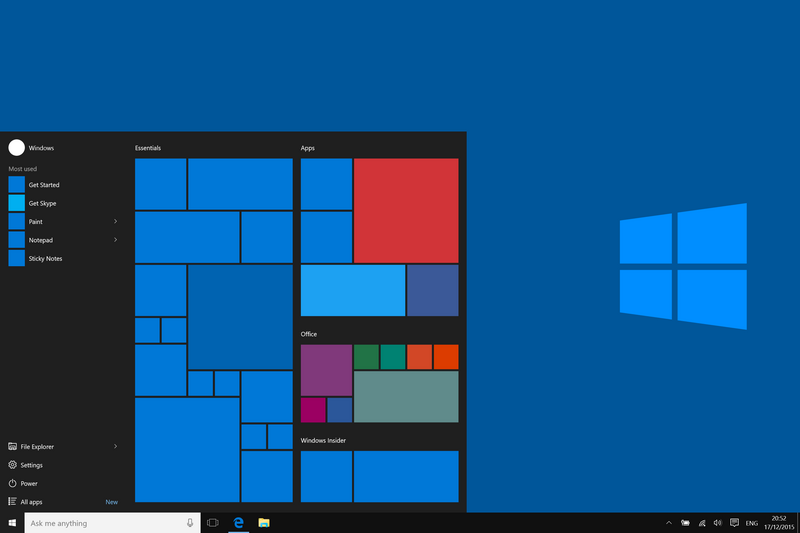
Windows 10, released in July 2015, followed in the footsteps of Windows 8 and marked a notable change in Microsoft’s operating system strategy. It responded directly to user feedback and criticism of its predecessor, with one of the standout features being the return of the Start menu—a familiar and much-loved part of previous Windows versions. The updated Start menu not only brought back traditional navigation but also allowed users to pin apps and display live tiles, combining the classic with modern functionality.
The introduction of “Windows as a Service” signaled a shift from traditional version-based updates to a model where users receive regular updates, ensuring their systems stay current with the latest features and security patches. Additionally, the launch of Cortana, Microsoft’s digital assistant, added a personal touch to the OS. By enabling users to interact with their devices through voice commands, set reminders, and search for information both locally and online, Cortana enhanced productivity and user convenience.
Microsoft Edge was introduced as a faster, safer, and more web-friendly browser, designed to replace Internet Explorer. Built from the ground up, Edge aimed to deliver a smoother browsing experience with modern web standards in mind. Meanwhile, Windows 10 made significant strides in multitasking with the addition of virtual desktops. This feature enabled users to create separate workspaces, making it easier to organize open applications and switch between tasks seamlessly.
Task View, which worked alongside virtual desktops, provided an overview of all open windows and desktops, enhancing workflow and productivity. Security was a key focus, with the introduction of Windows Hello – a biometric authentication system that allowed users to log in securely via facial recognition or fingerprint scanning. Windows Defender was also revamped into Windows Security, providing stronger protection against malware and viruses.
The Anniversary Update, released in August 2016, brought even more features, such as the Windows Ink workspace. This tool catered to users with touch-enabled devices, enabling them to draw, annotate, and take notes directly on their screens. Later updates continued to refine the experience, with enhancements to the Start menu, Cortana, and Edge, along with new features like Timeline, which let users easily pick up where they left off on different devices.
